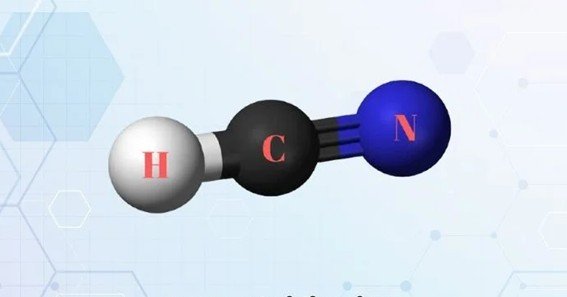
The Lewis structure of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a fundamental representation in chemistry that illustrates the arrangement of valence electrons among atoms within the molecule. Understanding this structure provides insights into HCN’s bonding, geometry, and chemical properties.
Drawing the HCN Lewis Structure
To accurately depict the Lewis structure of HCN, follow these steps:
- Calculate Total Valence Electrons:
- Hydrogen (H): 1 valence electron
- Carbon (C): 4 valence electrons
- Nitrogen (N): 5 valence electrons
- Total: 1 + 4 + 5 = 10 valence electrons
- Determine the Central Atom:
- Carbon is less electronegative than nitrogen and can form multiple bonds, making it the central atom.
- Arrange Electrons to Form Bonds:
- Place a single bond (2 electrons) between carbon and hydrogen.
- Place a triple bond (6 electrons) between carbon and nitrogen to satisfy the octet rule for both atoms.
- This uses 8 electrons, leaving 2 electrons to be placed as a lone pair on the nitrogen atom.
The resulting structure is: H–C≡N:
Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles
HCN has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180°, resulting from the arrangement of electron pairs around the central carbon atom.
Hybridization
The carbon atom in HCN undergoes sp hybridization, forming two sp hybrid orbitals. One overlaps with the 1s orbital of hydrogen, and the other overlaps with an sp hybrid orbital of nitrogen, facilitating the formation of sigma bonds. The remaining unhybridized p orbitals on carbon and nitrogen form two pi bonds, constituting the triple bond between carbon and nitrogen.
Polarity
HCN is a polar molecule due to the significant electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen, creating a dipole moment with a partial negative charge on the nitrogen atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom.
Conclusion
Understanding the Lewis structure of HCN is essential for grasping its bonding, geometry, and chemical behavior. This knowledge is foundational for predicting molecular interactions and reactivity in various chemical contexts.
FAQ
- What type of bonds are present in HCN?
- HCN contains a single sigma bond between hydrogen and carbon, and a triple bond (one sigma and two pi bonds) between carbon and nitrogen.
- Why is HCN linear in shape?
- The linear shape results from sp hybridization of the carbon atom, leading to a bond angle of 180°.
- Is HCN a polar molecule?
- Yes, due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen, HCN has a net dipole moment, making it polar.
- How many lone pairs are present in the HCN molecule?
- There is one lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in HCN.
- What is the significance of the Lewis structure in understanding HCN?
- The Lewis structure helps visualize the arrangement of electrons, predict molecular geometry, and understand the bonding and properties of HCN.
Uncover something cool here a-serbian-film-2160p-rar
- The Lewis structure helps visualize the arrangement of electrons, predict molecular geometry, and understand the bonding and properties of HCN.